Afro hair transplant is a specialized hair restoration procedure designed
for individuals with Afro-textured hair, using advanced extraction
techniques and specialized equipment to safely harvest curved and coiled
hair follicles. Specialized tools and techniques are required for Afro
hair to minimize transection rates that can reach 80% with conventional
methods developed for straight hair. Afro hair transplants cost between
$3,000 and $25,000 depending on location and achieve success rates above
90% when performed with proper techniques.Afro hair transplants address
unique challenges posed by curved follicular structures that sit at acute
angles beneath the scalp surface. The C-shaped or helical configuration of
Afro-textured hair follicles requires surgeons to use specialized curved
punches, larger diameter instruments, and modified extraction protocols to
prevent follicle damage during harvesting. Despite lower average hair
density compared to straight hair, the curly morphology creates excellent
coverage and fullness after transplantation.The procedure effectively
treats androgenetic alopecia, traction alopecia, central centrifugal
cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), and scarring from chemical treatments or
tight hairstyling practices. With proper technique, advanced equipment,
and experienced surgeons, individuals of African descent can achieve
natural, permanent hair restoration results.
Key points:
- Afro hair transplant uses specialized techniques for curved, coiled hair follicles
- Costs range from $3,000 to $25,000 depending on country and technique
- Success rates reach above 90% with proper methods
- Maximum 4,500 grafts can be transplanted in single session
- Procedure takes 6-8 hours on average
- Requires larger punch sizes (1.3mm-1.6mm) than straight hair
- Works for scalp hair, beard, and body hair restoration
- Test grafting recommended to assess keloid risk
What is a hair transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that moves individual hair follicles from areas resistant to balding (donor site) to areas experiencing hair loss (recipient site) on a patient’s scalp. The procedure falls under reconstructive plastic surgery and provides a permanent solution for various types of hair loss.What is Afro hair transplant?
Afro hair transplant is a specialized hair restoration technique that uses modified extraction methods or equipment designed to safely harvest and implant the curved, coiled, or helical hair follicles characteristic of Afro-textured hair. Unlike standard hair transplants performed on straight hair, Afro hair transplants must account for the unique curl pattern where follicles can curve at diameters of 3mm-4mm beneath the skin. To account for this curve, hair transplant surgeons must use modified techniques or equipment to safely harvest and implant Afro-textured hair.How much does Afro hair transplant cost?
Afro hair transplants cost between $3,000 and $25,000 depending on the country, technique, and number of grafts. In Western countries such as the USA, UK, and Germany, the average cost ranges from $15,000 to $25,000. In countries like Turkey, Afro hair transplants cost around $2,000 to $5,000 on average. Hair Transplat Cost.Are Afro hair transplants more expensive?
No, even though Afro hair transplants require specialized tools, modified techniques, and specialized experience on the surgeon’s and technician’s parts, it is priced similarly to hair transplants for straight hair. If your clinic is charging more for an Afro hair transplant compared to hair transplants for straight hair, it’s discrimination based on ethnic origin.What is the success rate of Afro hair transplant?
The success rate of Afro hair transplant with specialized techniques is above 90% when performed by experienced surgeons using proper equipment. Studies show that maximum transection rates of less than 10% can be achieved with skin-responsive FUE devices and proper technique, compared to transection rates (hairs los during harvesting and graft preparation) of 6%-80% reported with conventional methods developed for straight hair. The success of Afro hair transplants depends on multiple factors including the surgeon’s experience with Afro-textured hair, proper punch size selection, extraction angle accuracy, skin thickness assessment, graft preparation protocols, and the hair’s degree of curliness.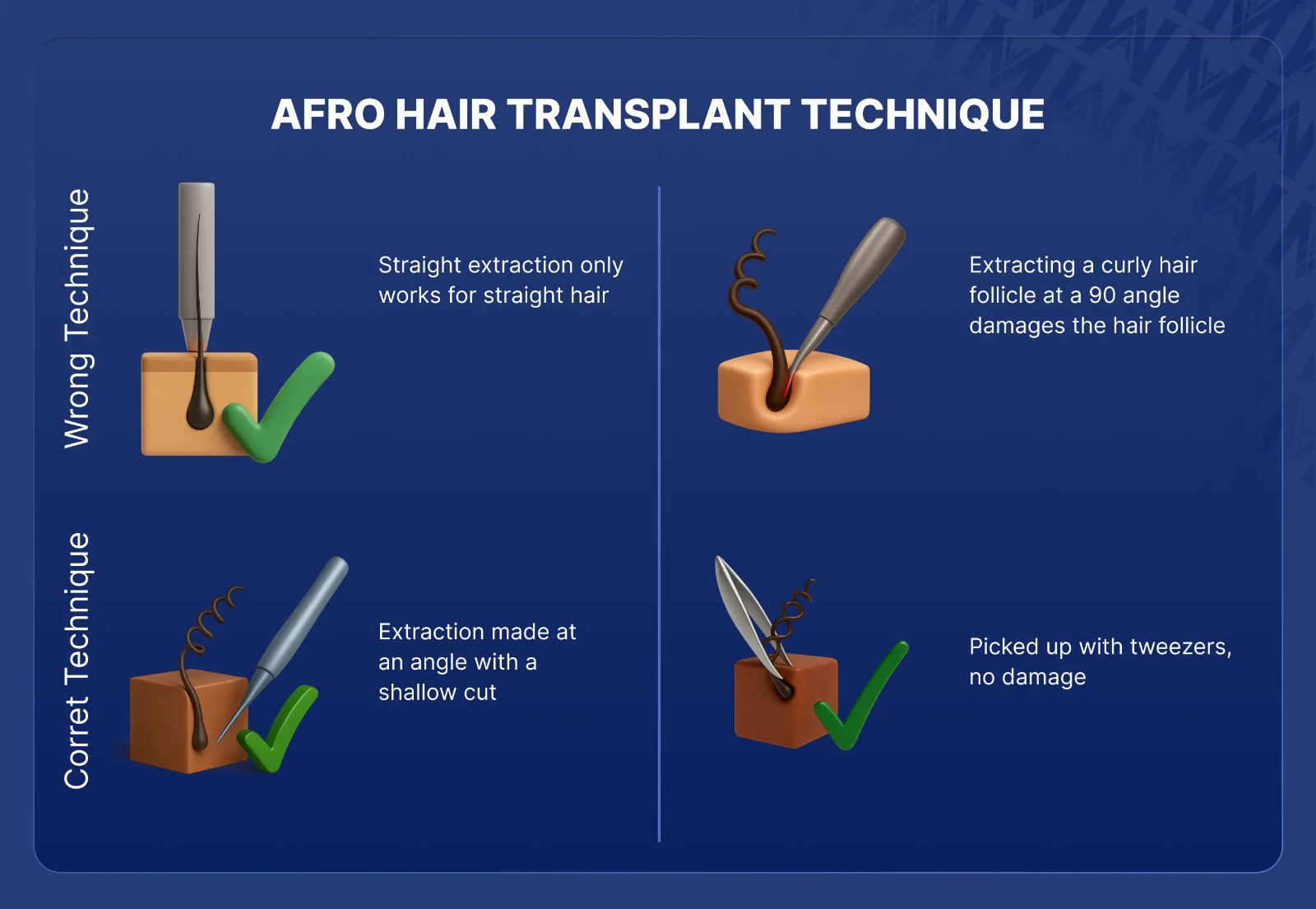
How does Afro hair transplant work?
Afro hair transplant works through a specialized three-phase process of assessment, extraction, and implantation designed specifically for curved follicular structures. The procedure uses the FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) method with modifications for Afro-textured hair characteristics. During the hair & scalp analysis phase, patients are assessed based on their skin thickness and hair texture. As a general rule of thumb, as the skin gets thicker and the hair gets more coiled and coarse in texture, more modifications are required to safely transplant the hair. During extraction, specialized punches enter the scalp at acute angles matching the hair’s exit angle to follow the curved follicular path. Grafts are extracted to mid-dermis depth only, then gently removed with forceps to prevent transection of the curved lower portion.
The Afro hair transplant process follows these steps:
- Pre-op tests, hair and scalp analysis
- Hairline design customized for African features
- Shaving the donor area
- Local anesthesia administration
- Follicular unit extraction with specialized curved or skin-responsive punches
- Graft preparation using curved DermaBlades
- Recipient site creation
- Graft implantation at proper angles
- Recovery and post-op instructions
- First wash and healing monitoring
How long does Afro hair transplant take?
An Afro hair transplant takes about 6-8 hours on average. The duration may be longer than standard hair transplants due to the increased care required during extraction to prevent transection of curved follicles, careful angle assessment for each graft, and meticulous graft preparation using curved blades.Can Afro hair transplant be done with body hair?
Theoretically, Afro hair transplants fom body hair to the scalp is possible but will have poor results as the body hair texture is significantly different from the hair texture on the scalp. A more suitable approach would be beard to head hair transplant.Does Afro hair transplant work for beard transplants?
Yes, Afro hair transplant techniques works for the transplantation of scalp hair to the beard area.Does Afro hair transplant work for eyebrow transplants?
Theoretically, eyebrow transplant with Afro hair texture is possible but results may not be satisfactory. The biggest challenge of an Afro eyebrow transplant is to find hairs similarly textured to the eyebrows on the patient’s body.What makes Afro hair transplant different from other hair transplants?
Afro hair transplant differs from standard hair transplants in tool requirements, extraction techniques, and equipment specifications necessary to safely harvest curved follicular structures. The fundamental difference lies in the C-shaped or helical configuration of Afro-textured hair beneath the scalp surface.
Key differences include:
- Specialized punches: Skin-responsive flared punches, curved non-rotary punches, or textured rotating punches should be used to avoid damaging hair follicles
- Larger punch diameters: If special punch tips are not available, surgeons should use larger sizes of standard punches
- Modified extraction angles: Must match acute entry angles to follow the curved follicular path of Afro hair follicles
- Shallower incisions: During extraction and implantation, incisions are made shallower to accommodate the curl pattern.
- Curved graft preparation tools: Using curved or flexible blades during graft preparation to reduce transection rates
- Longer procedure time: Additional care required increases surgery duration
- Lower density with more coverage: More coverage can be achieved with less hair
- Higher keloid risk: People of African descent are more likely to develop keloid scarring, which needs to be accounted for
What is the maximum number of grafts possible with Afro hair transplant?
The maximum number of grafts possible in a single Afro hair transplant session is 4,000 grafts. This number may seem low, but patients of African descent can achieve satisfactry results with good coverage at lower graft counts.How are Afro hair transplant grafts counted?
Afro hair transplant grafts are counted as follicular units containing 1-4 individual hair follicles. Individuals of African descent typically have 3 follicles per follicular unit on average, compared to 2 in Caucasian individuals, which results in higher total hair counts despite lower follicular unit density.How is donor area capacity calculated for Afro hair transplant?
Donor area capacity for Afro hair transplant is calculated during pre-operative microscopic scalp analysis that evaluates follicular unit density, hair caliber, scalp laxity, and the degree of follicular curvature.How is the hairline designed for Afro hair transplant?
The hairline design for Afro hair transplant follows masculine or feminine aesthetic principles appropriate for African facial features.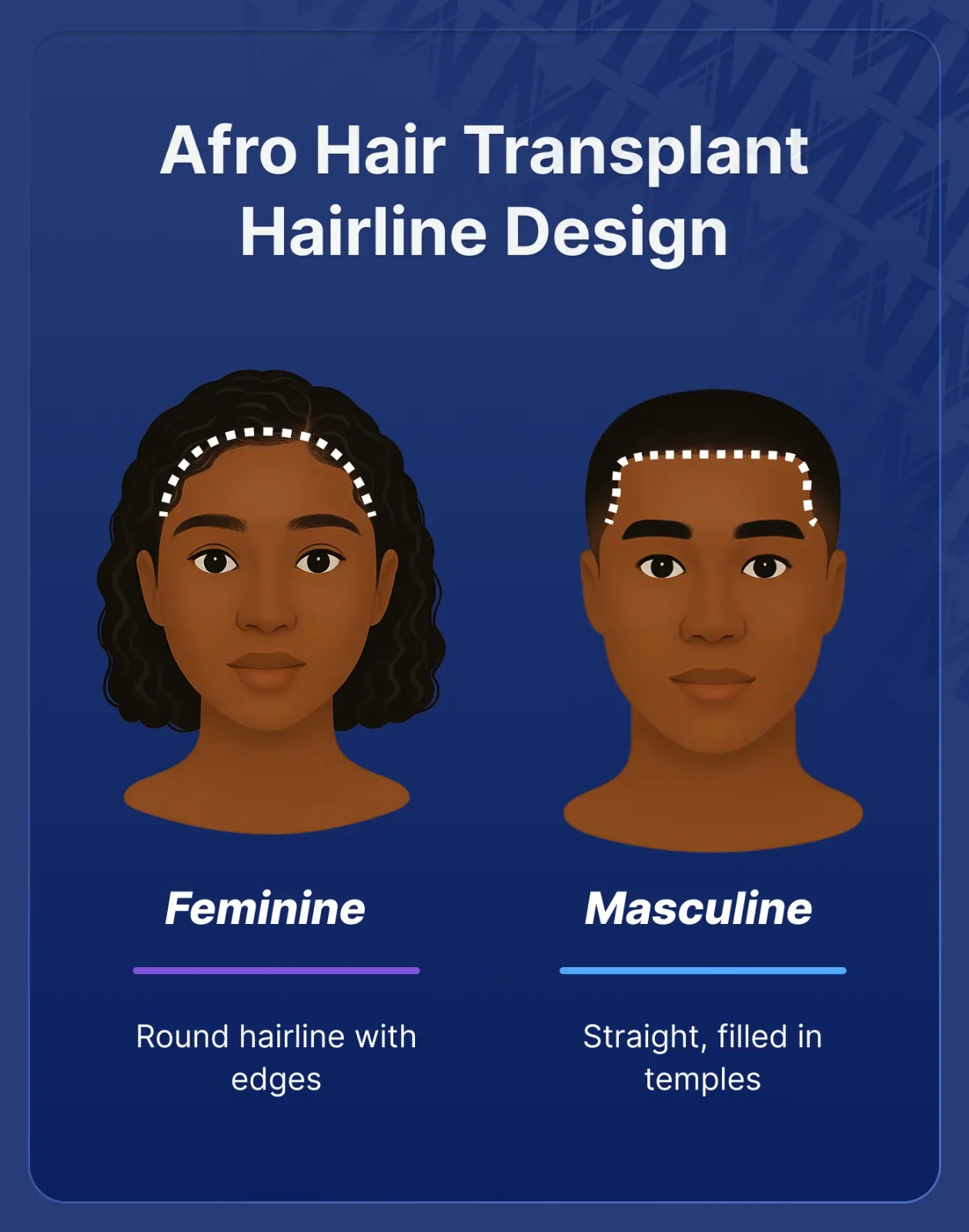 For men, the hairline is designed straight across or with minimal
temporal recession, typically positioned 8-10cm from the glabella. For
women, a lower, rounded hairline with soft irregularity is created to
mimic natural edges.
For men, the hairline is designed straight across or with minimal
temporal recession, typically positioned 8-10cm from the glabella. For
women, a lower, rounded hairline with soft irregularity is created to
mimic natural edges.
Get a Free Hair Analysis
Find out how many grafts you need — for free. Our team will get back to you in minutes.Who is a good candidate for Afro hair transplant?
You are a good candidate for Afro hair transplant if you:
- Are between ages 18-65
- Have stable hair loss pattern (Norwood 2-6)
- Have sufficient donor hair quality and density
- Are in overall good health without active scalp conditions
- Have realistic expectations about results
- Do not have active inflammatory scalp disease
- Have no personal or family history of keloid formation
Do you need to shave your hair for Afro hair transplant?
Yes, you need to shave your recipient area for proper extraction of Afro textured hair. The recipient are may be left long depending on your case.What is the best age for Afro hair transplant?
The best age for Afro hair transplant is between 25 and 60. Between these ages, most individuals have established hair loss patterns suitable for surgical planning, adequate wound healing capacity, and realistic expectations about long-term outcomes.Which hair loss types can Afro hair transplant work for?
Afro hair transplant can work for restoring hair loss from:
- Androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness)
- Traction alopecia (if hair loss is permanent)
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA) (if inactive for 9-12 months)
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia (if inactive and stable)
- Scarring from chemical treatments or burns
- Failed previous hair transplants
- Receding temples and hairline
- Crown thinning
Does Afro hair transplant work for women?
Yes, Afro hair transplant works effectively for women experiencing female pattern hair loss, traction alopecia from tight hairstyles (braids, weaves, extensions), or inactive CCCA. Women of African descent are excellent candidates when they have stable donor hair and realistic expectations.Can Afro hair transplant be done with thin donor hair?
Thin donor hair is not recommended for Afro hair transplant because miniaturized follicles have lower survival rates and are more susceptible to transection during extraction due to reduced structural integrity.What are the alternatives to Afro hair transplant?
The alternatives to Afro hair transplant include:
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): Strip harvesting avoids curved extraction challenges but leaves a linear scar, which clashes with hair styling practices preferred by people with Afro hair textures and is more likely to develop a keloid scar, making it a less than ideal for Afro hair transplants.
- Medical therapy: Minoxidil 5% and finasteride for androgenetic alopecia
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy: Growth factor injections for hair density
- Scalp micropigmentation: Tattoo technique to mimic the look of shaved hair follicles
- Hairpieces and wigs: Non-surgical cosmetic solutions that are also used after hair transplantation as protective styling options
- Hair systems: Custom-fitted prosthetic hair
What makes Afro hair unique for hair transplantation?
Afro hair is unique for hair transplantation due to its curved or helical follicular structure, lower density, larger follicular units, and distinct skin characteristics. The fundamental difference lies in the C-shaped configuration beneath the scalp surface, where the follicle curves at acute angles creating a subterranean curl pattern.
Unique characteristics include:
- Follicle structure: Curved, coiled, helical, or spiraled rather than straight
- Follicular unit density: Average 3 follicular units per cm² compared to 5 for Caucasian hair
- Hairs per follicular unit: Average 3 hairs growing from a follicular unit compared to 2 in Caucasian follicular units
- Subterranean curl diameter: 3mm-4mm C-curve beneath skin surface
- Hair shaft characteristics: Flattened, ribbon-like cross-section
- Scalp characteristics: Often thicker, firmer skin, prone to keloid scars which makes the surgery more difficult
- Coverage efficiency: Curly morphology creates a fuller appearance despite lower density & hair count
- Minimal color contrast: Less contrast between scalp and hair enhances coverage appearance
How does the curl pattern of Afro hair affect transplant results?
The curl pattern of Afro hair affects transplant results by requiring larger extraction tools, modified techniques, and longer surgery time, but ultimately provides excellent coverage and natural appearance due to the curly morphology. The curved follicular structure increases transection risk during extraction but creates superior aesthetic density after implantation. The C-shaped subterranean curl means surgeons cannot predict follicle direction beneath the skin surface, necessitating specialized tools or techniques to navigate the curved path. However, once transplanted, the curly hair texture provides more scalp coverage per follicle than straight hair, partially compensating for lower follicular density.
What is the difference between Afro hair and straight hair for transplantation?
The differences between Afro hair and Caucasian hair for transplantation are as follows:| Afro Hair Transplant | Caucasian Hair Transplant | |
|---|---|---|
| Follicle structure | Curved/coiled/helical | Straight/wavy |
| Follicular unit density | 3 units/cm² | 5 units/cm² |
| Hairs per follicular unit | 3 follicles/unit | 2 follicles/unit |
| Transection risk | 6 up to 80% with improper technique | 5-10% |
| Keloid formation risk | 4-16% | 1-4% |
| Coverage appearance | Better coverage with less hair | Standard coverage |
| Scalp-hair color contrast | Less contrast enhances fullness | Higher contrast |
| Extraction complexity | Requires specialized tools or techniques | Standard tool and techniques are sufficient |
What should you do before Afro hair transplant?
Before Afro hair transplant, discontinue medications as directed by your doctor, avoid smoking, alcohol, and recreational drugs for at least 2 days (preferably 2 weeks), and stop finasteride for 7 days and minoxidil for 10 days before surgery. Consult your doctor about stopping blood thinners 7 days before the procedure. Additionally, avoid chemical relaxers, hair dyes, and heat treatments for at least 2 weeks before surgery. Inform your surgeon about any personal or family history of keloid formation to determine if test grafting is necessary.How to find the best Afro hair transplant clinic?
When selecting an Afro hair transplant clinic, verify their specific experience with Afro-textured hair, not just general FUE experience. Review before/after photos of patients with similar hair types (4a, 4b, 4c), examine their transection rates for curved hair, and confirm they use specialized equipment or technique. Choose a clinic that offers test grafting for keloid-prone patients, provides realistic graft estimates based on curved hair challenges, has protocols for managing keloid risk, offers comprehensive aftercare, and maintains transparency about the unique challenges of Afro hair transplantation.What questions to ask during Afro hair transplant consultation?
You can ask these questions during an Afro hair transplant consultation: “How many patients with my specific hair type have you treated?” “What is your average transection rate for Afro-textured hair?” “Which specialized punches and techniques do you use for curved hair?” “What is your protocol for preventing and managing keloid formation?” “Can you show me before/after photos of patients with hair similar to mine?” “Do you recommend test grafting in my case?” “How many grafts can safely be extracted from my donor area?” Buton: 64 Questions to ask your Turkish Hair Transplant ClinicWhat should you avoid after Afro hair transplant?
After Afro hair transplant, avoid smoking for 2 weeks, caffeine for 2 days, direct sun exposure for 2 months, and excessive salt or spice consumption to reduce inflammation. Refrain from physical activity and exercise for 1 month, avoid sweating for 10 days, and do not shave the recipient area for 2 months. Keep your head elevated while sleeping using a neck pillow, wash your head and body separately for 10 days, wear loose button-up clothing to prevent contact with the scalp, and avoid hair dye for 6 months.What is the recovery process after Afro hair transplant?
The recovery process after Afro hair transplant requires minimal activity with elevated sleep position for the first 24-48 hours. From days 3-7, gentle washing begins and scabs start forming. By days 7-14, scabs fall off and temporary shedding begins. Normal activities resume between weeks 2-4. The shedding phase continues for months 1-3, followed by new growth emergence and strengthening between months 3-12.How long does the donor area take to heal after Afro hair transplant?
The donor area takes 7-10 days to heal after Afro hair transplant using FUE extraction. The SRFD punch creates less-everted wounds that heal faster through primary closure rather than secondary healing, resulting in minimal visible scarring.Does Afro hair transplant heal faster?
No, Afro hair transplants do not heal faster compared to hair transplants for straight hair. However, if improper technique is used during surgery, it can take longer to heal.When can you get a haircut after Afro hair transplant?
You can get a haircut using scissors only at 4 weeks after Afro hair transplant. Clippers with guards can be used on the donor area at 8 weeks, but the recipient area should not be cut with clippers until 4 months post-surgery to protect vulnerable grafts.What are the side effects of Afro hair transplant?
The most common Afro hair transplant side effects are swelling, discomfort, itchiness, and scabbing. Shock loss can occur in the recipient area. Serious complications such as infections, poor graft survival, and keloid formation are rare but more common in Afro hair transplants than other hair types.How long does swelling last after Afro hair transplant?
Swelling after Afro hair transplant lasts approximately 5-7 days. Swelling may be more pronounced than in straight hair transplants due to longer surgery time and potential for thicker skin characteristics.Does Afro hair transplant leave scars?
Afro hair transplant leaves minimal scars in the donor area when performed with proper FUE techniques. However, individuals of African descent have higher keloid formation risk (4%-16%), making proper patient and technique selection crucial.Does Afro hair transplant cause shock loss?
Yes, Afro hair transplant can cause shock loss like any hair transplant method. Shock loss occurs because surgical stress causes hair to enter the catagen (shedding) phase, with hair visibly shedding 2-6 weeks post-surgery. The roots remain healthy and regrowth begins around 120 days (4 months).Can Afro hair transplant cause keloid scarring?
Yes, people of African descent are 4 times more likely to develop keloid scarring than transplants in other populations, with incidence rates of 4%-16% in individuals of African descent compared to 1-4% in Caucasian individuals. This risk makes test grafting, proper surgical technique, and prompt post-operative care critical. Keloid formation can occur in both donor and recipient areas. Risk factors include personal or family history of keloids, younger age, and previous surgical sites. Preventive measures include test grafting, immediate post-surgical prophylaxis (topical corticosteroids, silicone gel sheeting, pressure therapy), and avoiding areas with previous keloid formation.When will you see Afro hair transplant results?
You will start seeing growth around 5-6 months after Afro hair transplant and reach full results between 12-18 months. Initial growth phase occurs during month 1, but transplanted hair sheds during months 2-3 as part of the natural process. New hair growth emerges between months 4-6, with noticeable improvement by months 7-9 and fuller growth developing thereafter.Will transplanted Afro hair maintain its curl pattern?
Yes, transplanted Afro hair maintains its original curl pattern and texture from the donor area. The follicle’s genetic characteristics, including curl formation, remain unchanged after transplantation. The C-shaped or helical growth pattern persists, providing the same natural appearance as the donor hair.How thick does transplanted Afro hair grow?
Transplanted Afro hair grows with the same thickness and diameter as the donor hair. Grafts containing multiple follicles may appear thicker because 2-3 hairs emerge from one location, creating more volumetric density than single follicle grafts.Can transplanted hair go grey after Afro hair transplant?
Yes, transplanted hair can go grey after Afro hair transplant following the same natural aging process as indigenous hair. The hair follicle’s pigment production decreases over time, resulting in gradual greying.Is Afro hair transplant permanent?
Afro hair transplant results are permanent for successfully transplanted follicles. Grafts relocated from DHT-resistant donor areas maintain their genetic resistance to androgenetic alopecia. However, 5%-10% graft loss is normal, and existing non-transplanted hair may continue thinning.Can you lose transplanted hair after Afro hair transplant?
You can lose 5%-10% of transplanted hair after Afro hair transplant, which is normal and accounted for during surgical planning. The primary survival rate ranges from 90%-95% depending on technique, surgeon skill, graft handling, and individual healing factors. Additional hair loss beyond this range likely represents indigenous hair loss rather than transplanted follicle failure.Can Afro hair transplant be repeated if needed?
Yes, Afro hair transplant can be repeated if sufficient donor hair remains, results are unsatisfactory, or continued hair loss creates new areas requiring coverage. The maximum safe extraction limit across multiple hair transplant procedures depends on donor density and previous extraction density.What are the risks and complications of Afro hair transplant?
The risks and complications of Afro hair transplant include high transection rates with improper technique (6%-80%), keloid formation (4%-16% incidence), poor graft survival in scarred areas, infection, excessive bleeding, postoperative pigmentation changes (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation), folliculitis keloidalis, and poor aesthetic results from inadequate density. Specific risks elevated in Afro hair transplants compared to straight hair include higher keloid propensity requiring test grafting and prophylactic treatment, increased transection risk without specialized equipment, potential for hyperpigmentation during healing, and challenges achieving adequate density with lower baseline follicular unit counts.What causes high transection rates in Afro hair transplant?
High transection rates in Afro hair transplant are caused by inadequate punch diameters, incorrect extraction angles, conventional punch designs, excessive extraction depth, and insufficient surgeon experience with curved follicular structures. When punch diameter is smaller than the subterranean curl width (C-curve), the punch blade cuts through the curved follicle portion. Conventional straight punches cannot navigate the helical path, and punching to full follicle depth without accounting for curve direction results in follicle transection. Transection rates of 6%-80% have been reported with standard techniques, compared to less than 10% with specialized methods.What are the pros and cons of Afro hair transplant?
The pros and cons of Afro hair transplant are shown in the table below:| Advantages of Afro Hair Transplant | Disadvantages of Afro Hair Transplant |
|---|---|
| Higher follicle count per follicular unit (3 vs 2) | Requires specialized tools and techniques |
| Less color contrast enhances fullness | Higher technical difficulty and complexity |
| Can treat traction alopecia and CCCA | Gets more difficult with thicker skin and collier hair |
| Curly texture creates volume and density with less hair | Few surgeons specializing in this technique |
| Significantly lower transeciton rates with modern tools and techniques | Higher keloid formation risk |
| Best permanent hair loss solution available | Not suitable during active scalp inflammation |
Common causes of hair loss in people of African descent
Common causes of hair loss in people of African descent include androgenetic alopecia, traction alopecia, central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, chemical damage, acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, and frontal fibrosing alopecia. These conditions affect individuals of African descent at higher rates or with distinct presentations compared to other populations, requiring specialized treatment approaches and consideration for hair transplantation candidacy.
The most common hair loss types in people of African descent are:
- Androgenetic alopecia (male/female pattern baldness): Affects men in bitemporal recession and vertex patterns (Norwood scale) and women in diffuse central thinning (Ludwig scale). Responds to topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and hair transplantation. Surgical candidacy is excellent for stable patterns.
- Traction alopecia: Caused by chronic tension from tight hairstyles including braids, cornrows, weaves, extensions, ponytails, and dreadlocks. Primarily affects frontal hairline and temporal areas. Progresses from reversible follicular damage to permanent scarring if traumatic styling continues. Treatment requires cessation of traction-causing styles and hair transplantation once scarring is established.
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA): Progressive scarring alopecia beginning at crown/vertex and spreading centrifugally. Incidence ranges from 2.7% in African populations to 5.6%-16.2% in African-American women. Involves lymphocytic inflammation destroying follicles. Associated with tight hairstyling, chemical relaxers, and genetic predisposition. Requires suppression of inflammation with oral doxycycline, topical clobetasol, and intralesional corticosteroids for 9-12 months before hair transplantation.
- Chemical damage: Results from relaxers, straightening treatments, and color processing that weaken hair shafts. Can trigger or worsen CCCA. Causes hair shaft fragility, breakage, and potential follicular destruction. Treatment requires discontinuation of chemical treatments and adoption of protective hair care practices.
- Acquired trichorrhexis nodosa: Hair shaft disorder causing fragility and breakage from trauma, excessive manipulation, chemical treatments, and environmental factors. Presents as broken hairs of varying lengths. Treatment includes discontinuing traumatic practices, daily moisturizing with silicone products, and protective styling.
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA): Variant of lichen planopilaris affecting frontoparietal hairline and eyebrows. Women of African descent develop FFA at younger ages (40-42 years vs. 55.5-63 years in Caucasians) with distinct dermoscopic features including speckled follicular hyperpigmentation. Requires combination therapy with topical/intralesional corticosteroids, oral finasteride or dutasteride, and hydroxychloroquine. Hair transplantation considered after 12+ months of disease quiescence.


